First injectable nanoparticle generator could radically transform metastatic breast cancer treatment

A team of investigators from Houston Methodist Research Institute may have transformed the treatment of metastatic triple negative breast cancer by creating the first drug to successfully eliminate lung metastases in mice. This landmark study appears today in Nature Biotechnology (early online edition).
The majority of cancer deaths are due to metastases to the lung and liver, yet there is no cure. Existing cancer drugs provide limited benefit due to their inability to overcome biological barriers in the body and reach the cancer cells in sufficient concentrations. Houston Methodist nanotechnology and cancer researchers have solved this problem by developing a drug that generates nanoparticles inside the lung metastases in mice.
In this study, 50 percent of the mice treated with the drug had no trace of metastatic disease after eight months. That’s equivalent to about 24 years of long-term survival following metastatic disease for humans.
Due to the body’s own defense mechanisms, most cancer drugs are absorbed into healthy tissue causing negative side effects, and only a fraction of the administered drug actually reaches the tumor, making it less effective, said Mauro Ferrari, Ph.D, president and CEO of the Houston Methodist Research Institute. This new treatment strategy enables sequential passage of the biological barriers to transport the killing agent into the heart of the cancer. The active drug is only released inside the nucleus of the metastatic disease cell, avoiding the multidrug resistance mechanism of the cancer cells. This strategy effectively kills the tumor and provides significant therapeutic benefit in all mice, including long-term survival in half of the animals.
This finding comes 20 years after Ferrari started his work in nanomedicine. Ferrari and Haifa Shen, M.D., Ph.D., are co-senior authors on the paper, which describes the action of the injectable nanoparticle generator (iNPG), and how a complex method of transporting a nano-version of a standard chemotherapy drug led to never before seen results in mice models with triple negative breast cancer that had metastasized to the lungs.
“This may sound like science fiction, like we’ve penetrated and destroyed the Death Star, but what we discovered is transformational. We invented a method that actually makes the nanoparticles inside the cancer and releases the drug particles at the site of the cellular nucleus. With this injectable nanoparticle generator, we were able to do what standard chemotherapy drugs, vaccines, radiation, and other nanoparticles have all failed to do,” said Ferrari.
Houston Methodist has developed good manufacturing practices (GMP) for this drug and plans to fast-track the research to obtain FDA-approval and begin safety and efficacy studies in humans in 2017.
“I would never want to overpromise to the thousands of cancer patients looking for a cure, but the data is astounding,” said Ferrari, senior associate dean and professor of medicine, Weill Cornell Medicine. “We’re talking about changing the landscape of curing metastatic disease, so it’s no longer a death sentence.”
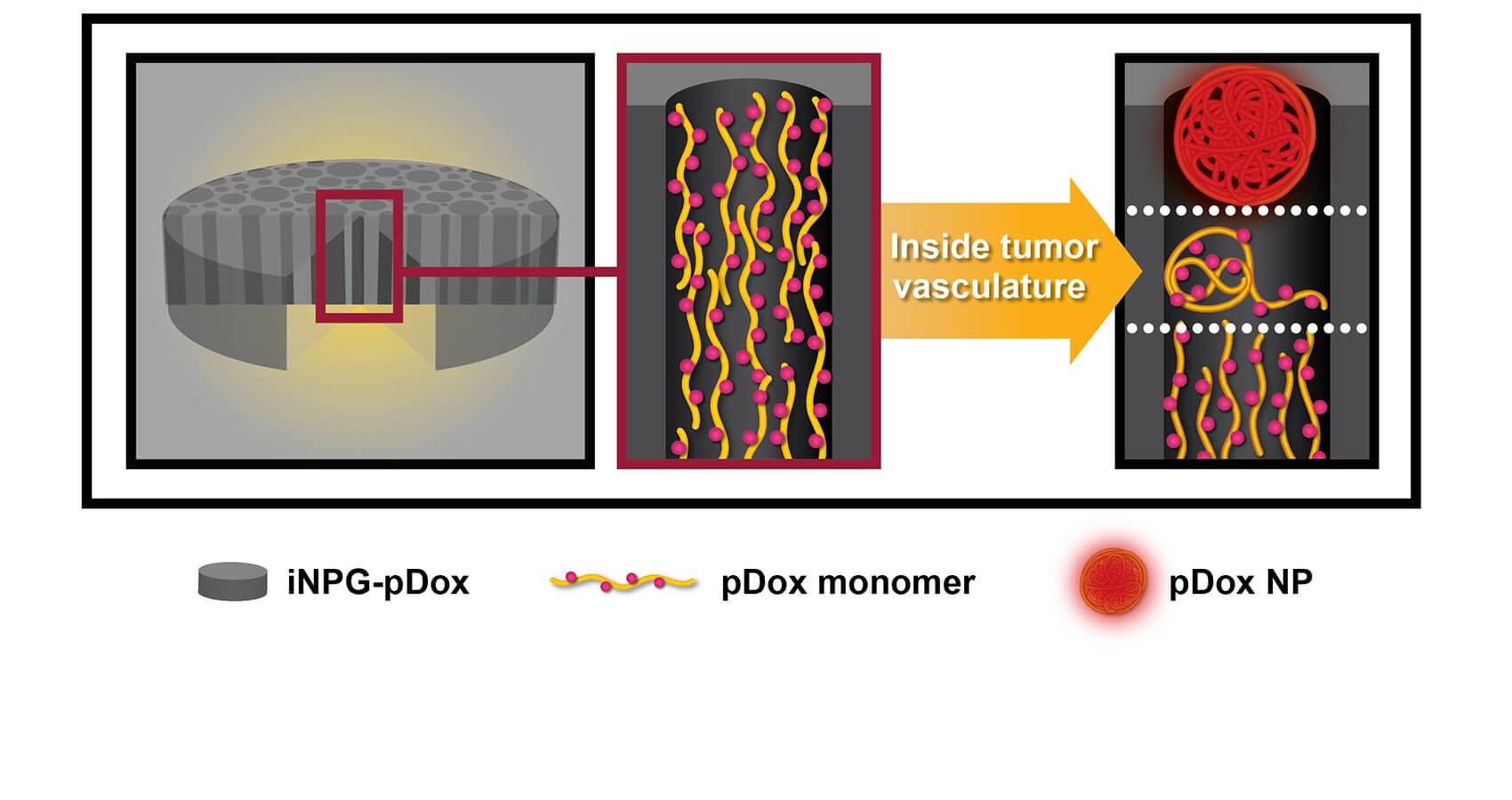
The Houston Methodist team used doxorubicin, a cancer therapeutic that has been used for decades but has adverse side effects to the heart and is not an effective treatment against metastatic disease. In this study, doxorubicin was packaged within the injectable nanoparticle generator that is made up of many components.
Shen, a senior member of the department of nanomedicine at Houston Methodist Research Institute, explains that each component has a specific and essential role in the drug delivery process. The first component is the nanoporous silicon material that naturally degrades in the body. The second component is a polymer made up of multiple strands that contain doxorubicin. Once inside the tumor, the silicon material degrades, releasing the strands. Due to natural thermodynamic forces, these strands curl-up to form nanoparticles that are taken up by the cancer cells. Once inside the cancer cells, the acidic pH close to the nucleus causes the drug to be released from the nanoparticles. Inside the nucleus, the active drug acts to kill the cell.
“If this research bears out in humans and we see even a fraction of this survival time, we are still talking about dramatically extending life for many years. That’s essentially providing a cure in a patient population that is now being told there is none,” said Ferrari, who holds the Ernest Cockrell Jr. Presidential Distinguished Chair and is considered one of the founders of nanomedicine and oncophysics (physics of mass transport within a cancer lesion).
The Houston Methodist team is hopeful that this new drug could help cancer physicians cure lung metastases from other origins, and possibly primary lung cancers as well.
Additional researchers who collaborated with Ferrari and Shen on the Nature Biotechnology paper were: Rong Xu, Guodong Zhang, Junhua Mai, Xiaoyong Deng, Victor Segura-Ibarra, Suhong Wu, Jianliang Shen, Haoran Liu, Zhenhua Hu, Lingxiao Chen, Yi Huang, Eugene Koay, Yu Huang, Elvin Blanco, and Xuewu Liu (Department of Nanomedicine, Houston Methodist Research Institute, Houston, Texas); Jun Liu (Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine, The University of Texas-Houston Medical School); and Joe Ensor (Houston Methodist Cancer Center, Houston, Texas).
The work was supported by grants from Department of Defense (W81XWH-09-1-0212 and W81XWH-12-1-0414), National Institute of Health (U54CA143837 and U54CA151668), and The Cockrell Foundation.
Nature Biotechnology is the highest rated publication in the Nature family of journals, with an impact factor of 41.5